Code Reader Podcast: P0340
Sharing the diagnostic approach of industry experts from our Maximizing Tools column, today’s Code Reader looks at a 2003 Mitsubishi Eclipse with the 4G64 2.4 liter and a complaint of a rough running condition and a no-start when warm. A DTC scan revealed DTC P0340.

Maximizing Tools: 4th Time’s a Charm – DTC P0340
The saying goes that lightning never strikes twice in the same place. Apparently, this was not the case for a Mitsubishi Eclipse 2.4 2003 4G64 that showed up with a complaint of a rough running condition and a no-start when warm.
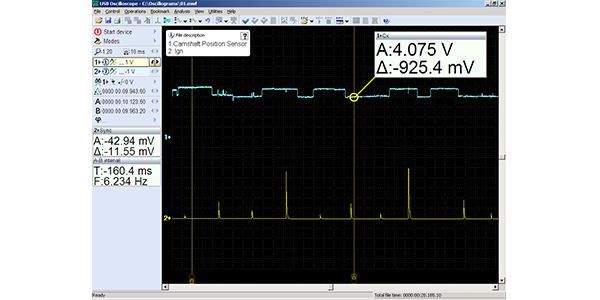
Pulling Codes: Signal No Longer Detected, The Story of Code P0340
This article will document the infamous P0340 code — Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction. This is a code that involves the CMP signal, and, in many situations, one may be tempted to replace the sensor right away. This article will attempt to provide a game plan of attack. It’s always wise to start with a
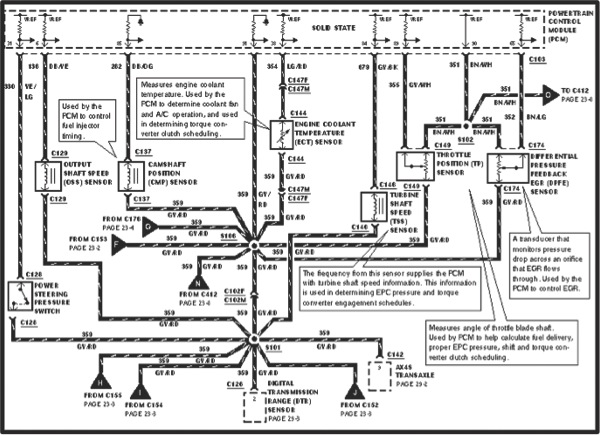
Tech Tip: Dodge Neon Sport Code P0340 Intermittently
Customer complains the vehicle bucks and misses intermittently while driving. Code P0340 is stored. This code may be caused by the camshaft position sensor.
Tech Tip: Lexus MIL On With DTC P0335 and/or P0340 Due To Low Battery Voltage
Applicable vehicles: 1994 and later models (non-hybrid and hybrid). Condition: Low battery voltage can contribute to a MIL On condition for P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit) and/or P0340 (Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit) due to inconsistent rotational speed of the engine’s crankshaft. Recommendations: • Review the vehicle’s freeze-frame data and verify if the battery voltage was
Diagnose, Repair, Repeat
An expert approach to a vehicle that would not cooperate.

Diagnosing Variable Valve Timing
Fully variable valve timing can be achieved only by using computer-operated solenoids to precisely control the intake and exhaust valve opening and closing events. Although the various combinations of valve timing events are theoretically infinite on an electronically controlled system, their applications are limited due to issues of cost and, in some cases, reliability.
Diagnostic Solutions: Variable Camshaft Timing And Back Pressure Issues
When the topic of variable valve timing (VVT) comes up in import repair shops, few realize that the concept of increasing low- and high-speed engine torque by automatically advancing and retarding valve timing isn’t a recent development. For example, I recently discovered an old variable camshaft timing gear that I bought during the 1960s featuring a torsion spring device that retards valve timing in response to the increased rotating torque needed to turn the camshaft at higher engine speeds.
Tech Feature: Hall Effect Sensor Diagnostics
Hall effect crankshaft position (CKP) and camshaft position (CMP) sensors are critical components of an engine management system. The inputs they provide enable the powertrain control module (PCM) to determine engine speed and position including where a given cylinder is within the four-stroke cycle.
Diagnostic Dilemmas: Solving No-Code Performance Complaints
For many diagnostic techs, nothing is more discouraging and time-consuming than dealing with a no-code driveability complaint. Today’s second-generation On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD II) can be extremely sophisticated because the OBD II powertrain control modules (PCMs) in modern vehicles have far more computing capacity than did the older, pre-1996 OBD I vehicles. Nevertheless, we occasionally have to deal with a no-code performance complaint on a modern OBD II vehicle.
