By Larry Carley
Technical Editor
Engines run hot! Almost a third of the heat energy produced by combustion is absorbed by the engine itself. That’s why engines need a cooling system. The cooling system absorbs the engine’s waste-heat and prevents the engine from overheating and self-destructing.
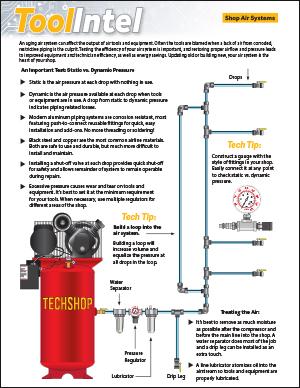
To get rid of the heat, the coolant inside the engine is pumped to the radiator by the water pump. The pump is usually located on the front of the engine and is driven by either the serpentine belt or the overhead cam timing belt. The pump itself is relatively simple, with a metal or plastic impeller mounted on a shaft. The shaft is supported in the water pump housing by a bearing and seal assembly.
On most engines, the water pump pulls coolant in through the lower radiator hose and routes it into the block and heads. The coolant then circulates back to the radiator through the thermostat housing and out the upper radiator hose. On some engines with “reverse flow” cooling systems, the pump routes the water into the cylinder heads first. Many water pumps also have additional inlet and outlet ports for heater hose and bypass connections.
Water pumps work hard. As the miles add up, so does the wear and tear on the pump shaft bearing, seal and impeller. Erosion inside the pump can wear away the vanes on the impeller, causing it to pump less efficiently as the impeller is eaten away. This may lead to engine overheating on hot days or when the engine is working hard. If the water pump seal becomes worn, coolant will leak past the pump shaft or out of the small vent hole on the housing. The loss of coolant will eventually cause the engine to overheat. If the pump shaft bearing fails or seizes, the shaft may break. Other symptoms of bearing wear may include pump noise (rumbling, chirping or growling) and fan or pulley wobble.
One way to identify a water pump with bad shaft bearings is to check pulley or fan play with the engine off. The pulley or fan should not move when wiggled sideways by hand. Pressure testing the cooling system can also reveal a leaky shaft seal inside the water pump.
Replacing a water pump that is leaking or failing is a repair that can’t be postponed for very long — especially if the pump is leaking coolant. Cooling system sealers usually can’t stop a shaft seal leak. Unless the steady loss of coolant is stopped or constantly replenished by adding more coolant, the engine will overheat. This should be avoided because overheating can damage the head gasket and other engine parts that are expensive to replace. Better to replace a failing water pump as soon as possible than to risk major engine damage!
A new or remanufactured water pump may cost anywhere from $20 to $100 or more depending on the application.
The labor required to change the pump will vary depending on the pump’s location. On some engines, the pump is relatively easy to change. On others (such as OHC engines where the pump is driven by the timing belt and the pump is located behind the timing belt), pump replacement requires a lot of disassembly. On some OHC applications, it’s probably a good ideal to go ahead and replace the timing belt if the pump has failed. If the belt has never been replaced or it has more than 60,000 miles on it, changing the timing belt and water pump at the same time saves the labor of having to do essentially the same job twice.
The condition of the cooling system should be carefully checked when replacing a water pump. Rust and sediment in the coolant can ruin a new pump, so the system should be flushed and refilled with fresh coolant if the old coolant is dirty or is more than a few years old.
Before installing the new part, compare the old and new pumps to make sure the pump housing, bolt configuration and fittings are the same. Also, compare the length of the pump shaft. Some engines use similar pumps that have different length shafts. This may cause interference or clearance problems if the wrong pump is installed.
Here’s something else to watch out for: On some engines with serpentine belts, the water pump turns in the opposite direction as the same pump does on an engine with conventional V-belts. The pumps may appear to be the same, but the impellers are backwards and are not interchangeable.
On rear-wheel drive vehicles that have a fan clutch, the lifespan of the clutch and water pump are about the same. Most experts recommend replacing both if either fails. Fan clutches lose their grip as they age and do not cool as efficiently as when they were new. This may lead to overheating on hot days or when pulling a heavier than normal load.
Other parts you may need include new hoses (upper and lower radiator loses, heater hoses and clamps), a new thermostat (recommended for high mileage engines or any engine that has overheated), possibly a new radiator cap (pressure test the old one to see if it holds the specified pressure), and fresh coolant.
When the water pump is installed, the pump mounting surface must be perfectly clean (no old gasket remnants) and dry to prevent leaks. The water pump gasket (if used) that fits between the pump housing and engine should be coated with sealer on both sides (sealer is not needed with rubber o-rings or molded rubber gaskets). If the pump mounts without a gasket, you will need the specified sealer: either an anaerobic sealer or RTV silicone. Water pump bolt threads that extend into the water jackets must be coated with sealer to prevent leaks. Bolts should be tightened to the recommended specs.