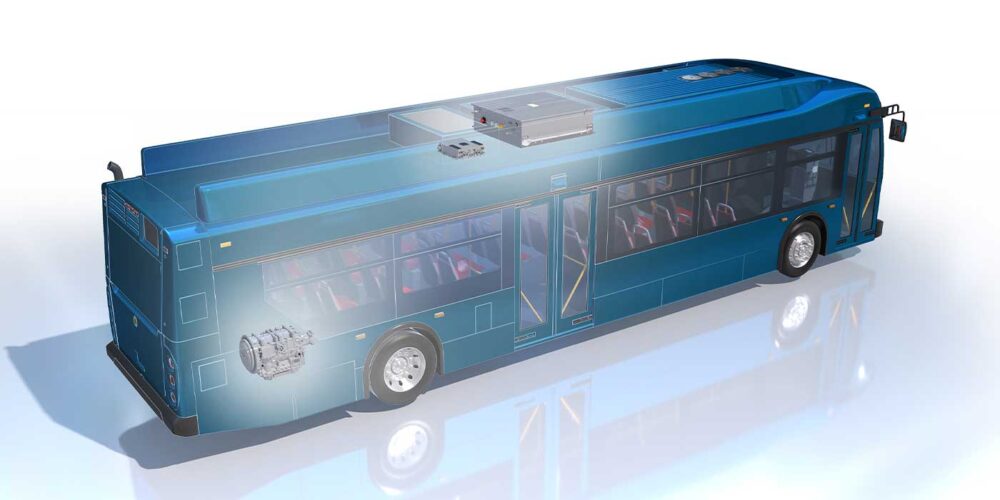
American Battery Solutions has signed a multi-year contract with bus manufacturer NFI Group Inc. to supply custom battery packs that will provide clean power for NFI subsidiary New Flyer’s newest 35-, 40- and 60-foot battery-electric transit buses. NFI is now launching ABS batteries into bus production for customer deliveries starting in the first quarter of 2024. The Li-Ion batteries were fully designed, tested and validated by ABS at its engineering and development center in Lake Orion, Michigan. The production of the batteries will be done at ABS’ manufacturing plant in Springboro, Ohio, the company said.
The market for electric buses in North America has now passed more than 5,480 zero-emission transit buses on the road or on order as of the end of 2022, according to CALSTART’s annual “Zeroing in on ZEBs” report. NFI expects that 40% of its 2025 production will be zero-emission buses.
“We are excited and proud to partner with NFI, a company at the forefront of electric- powered public transportation. This contract reflects NFI’s well-placed confidence in ABS’ ability to meet technical and performance requirements at a healthy volume with the competitive cost position,” said Subhash Dhar, ABS founder, chairman and CEO. “We have invested over $ 200 million in our state-of-the-art automated pack assembly line and facility, with the capacity to deliver the product NFI needs so that it can continue to lead the electrification of public transportation in North America.”
“Demand for battery-electric buses is accelerating, and NFI is leading the evolution to zero-emission public transportation in North America. Our partnership with ABS will provide NFI with the capacity, flexibility, and resiliency we need as we ramp up production at our facilities across North America,” said Paul Soubry, president and CEO of NFI. “ABS has made significant investments in their pack assembly and battery technology, providing NFI with industry leading solutions. We look forward to working together with ABS to advance battery technology within the public transportation industry.”
This scalable custom designed pack solution is based on the ABS ProLiance Intelligent Battery Series architecture and fits inside NFI’s existing battery enclosure design, providing an alternate source of supply for NFI’s battery-electric bus contracts and creating opportunity for technology enhancements, ABS said. Design and engineering have been led from ABS’ Michigan Innovation Center in Lake Orion, with the pack production scheduled to begin in the third quarter of 2023 at ABS’ Springboro manufacturing facility. ABS has secured the cell supply by partnering with cell makers in strategic alliances, which have resulted in the signing of long-term supply agreements that ensure cell supply through the end of the decade, ABS said.