th of the disc brake pads, replace the disc brake pads.

th of the disc brake pads, replace the disc brake pads.

The campaign aims to raise $65,000 through 1,000 donations of $65 each.
The Automotive Aftermarket Charitable Foundation (AACF) announced the launch of its 65th-anniversary fundraising initiative. Running through July 1, 2024, the campaign aims to raise $65,000 through 1,000 donations of $65 each. This impactful effort highlights the industry's commitment to taking care of its own, the AACF said.
From sudden illness and death to natural disasters, the foundation has provided assistance to industry professionals and their families during their darkest hours. As AACF celebrates its 65th year of service, it remains steadfast in its mission to provide financial support and resources to those in the automotive aftermarket industry in need, the organization said.
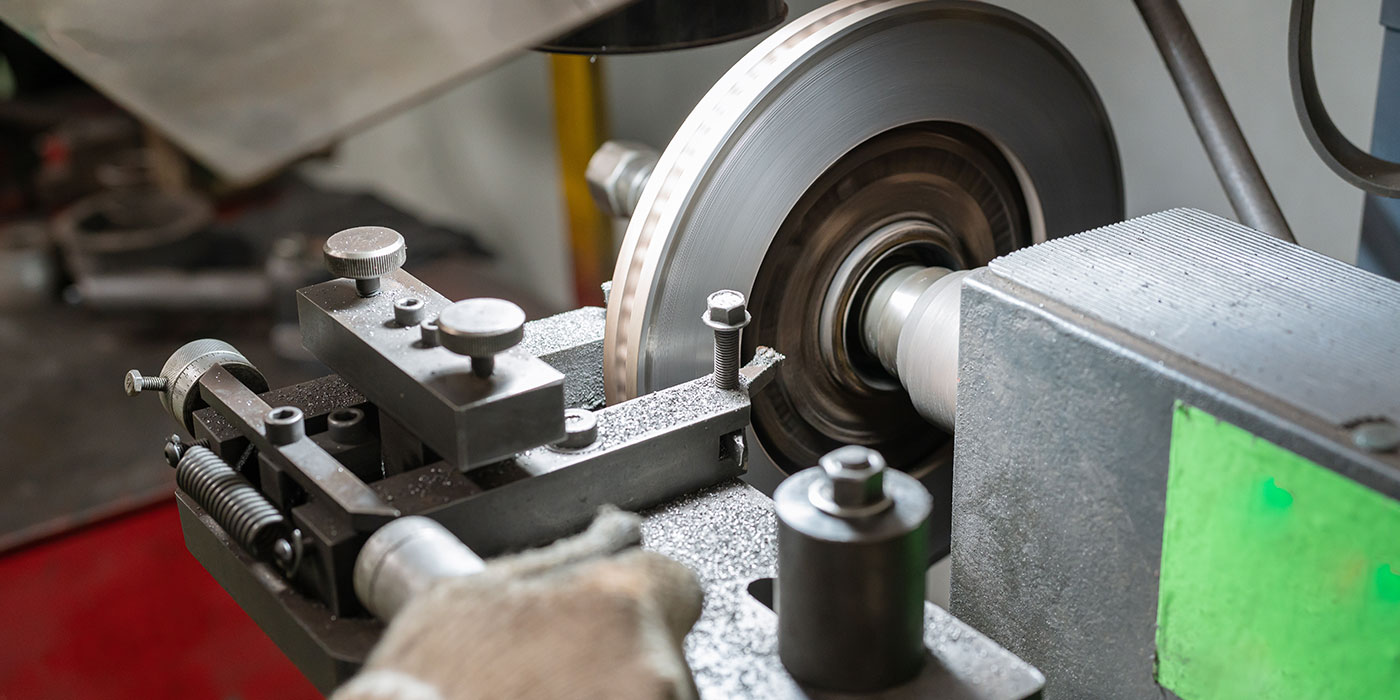
Resurfacing drums and rotors is a machining process with its own specific guidelines.

Oil type is just as important as oil capacity.

Steve Coffell, a technician at Auto World in Hazelwood, MO, says his Top 5 Favorite Tools are: Related Articles – Lisle 61860 Oil Filter Housing Torque Adapter – Mueller Kueps Presents Redesigned Sensor Tap Series – Lisle Low Profile Fuel Line Disconnect OTC Genisys Touch – Quick scan, bidirectional control Snap-on VANTAGE Pro –
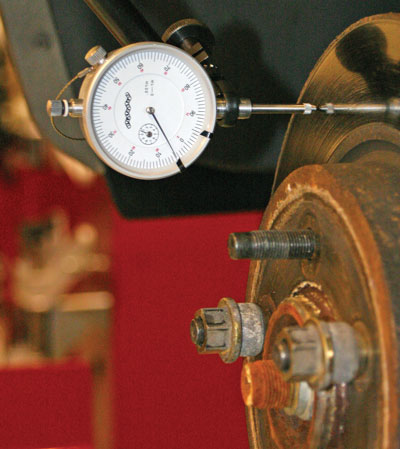
A wheel bearing that’s out of adjustment can reduce bearing life and can affect more than just the bearing. It’s important to adjust the wheel bearing endplay to the proper specifications. If the bearing set is adjusted too loose or too tight, it can cause the bearing to fail prematurely. There are a few types of assemblies, so using correct procedures and tools will ensure a comeback-free wheel bearing installation.
Grew company from small machine shop to global leader in car lifts and garage equipment.

To date, TOPDON has donated over $66,000 to aid organizations and schools that are dedicated to preparing the next generation of auto technicians around the world.

The event will be held on April 22-24, 2024 in Newport Beach, CA, at the VEA Newport Beach Marriott.

IDC5 CAR 76.5.0 is characterized by over 2600 new possible selections for the major makes on the market worldwide.
