Contamination always has negative connotations. For brake pads, it has dual meanings. First, it can mean a contaminated friction surfaces that alter friction levels and performance. Second, it can mean contamination to the environment from brake dust.
In this article, we will attempt explain both issues because both forms of contamination start when a brake pad is pressed into a rotor and friction is generated.
Friction and Dust
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of elements sliding against each other. In the case of cars and trucks, it is the brake pads pushing against a rotor that changes kinetic energy into heat.
Some friction materials use a different material for the bottom layer of the pad
If you could mount a microscope on a brake pad, you would see bits and pieces of the pad and rotor breaking away from the surfaces as they contacted the rotor. As this is happening, the heat is physically and chemically changing the exposed friction material and bits and pieces are being torn or sheared from the rotor and pad.
Some particles become part of the friction surface or the rotor while others are cast off to stick to wheels and eventually be washed down the drain and maybe into rivers and streams.
The bottom line is that for the brakes to function, the rotors and pads have to wear. Even a brake rotor’s metallurgy can determine how a pad wears.
The Secret Sauce of Friction
How the components in the friction material shear, break and interact during braking can determine a pad’s friction level, noise and wear characteristic.
A brake pad may require up to 20 different raw materials. Some raw components of a friction material are abrasive, while another components lubricate. Some components, like structural fibers and resins, hold the pad together, while other components tune the friction levels through various temperature ranges.
Tuning the components in a brake pad mix is like tuning a graphic equalizer on a stereo for the best sound. This is the black art of friction material formulation and why some pad manufacturers protect their recipes like Coke and KFC’s seven secret herbs and spices.
Two Types of Friction
So friction is friction right? Wrong. There are two types of friction when it comes to brakes.
A friction material has may different components. Kevlar fibers help to give the brake pad structure under high temperatures
Abrasive friction is the breaking of bonds of both the pad material and the cast iron of the disc when the caliper pushes them together. Adherent (or adhesive) pad material forms a very thin transfer layer of pad material on the surface of the rotor. The two surfaces are the same materials and generate friction by breaking or shearing the bonds in the pad.
Abrasive friction is the wearing of the pad and rotor to change forward motion into heat. Both components wear. Semi-met pads and some non-asbestos-organics use this type of friction.
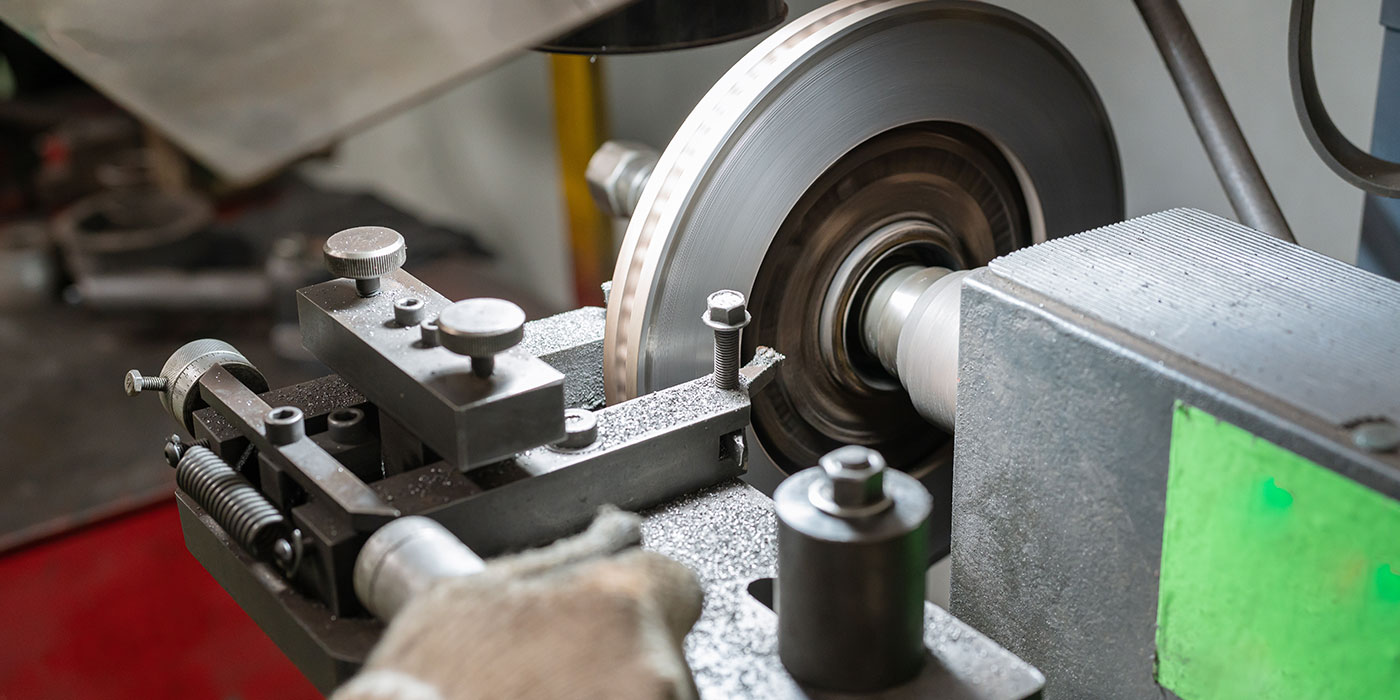
Adherent (or adhesive) pad material transfers a very thin layer of pad material onto the surface of the rotor. Ceramic and some NAO pads use this type of friction. The transfer layer is bonded to the rotor’s surface and cannot be washed away by water or wheel cleaners. The only way to remove it is by removing it with a brake lathe or abnormal heat.
The layer is always being worn and replenished by the brake pad during braking. These pads produce dust. Adherent friction is easier on rotors, but the pads become the primary wear component.
With this type of pad, it is critical to machine the rotor with the correct surface finish and follow the recommended break-in procedure so the transfer layer can be established.
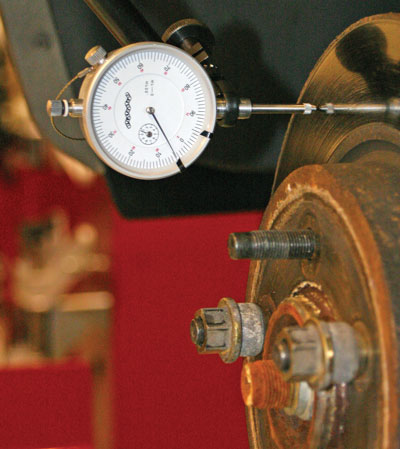
With both types of friction, it is critical for the rotor to have minimal runout. Abrasive friction materials will wear away at high spots creating disc thickness variation and pulsation. Adhesive or adherent friction material could deposit the friction material unevenly and cause brake judder.
Bad Stuff
Why do some pads use components that could be considered harmful to the environment and people? Part of the answer is that the effects on the environment of some components were not fully realized until a few decades ago.
Copper is used in brake pads as an abrasive, but two states have legislation limiting its content in brake pads. Copper performs several functions: it adds structural integrity to the brake pad material, reduces fade so that brakes remain effective through extended braking events, transfers heat efficiently, and helps brakes be more effective in cold weather. Copper also has properties that help prevent brakes from squeaking and shuddering.
But the brake dust from these pads is the leading cause of copper contamination in lakes and streams.
The same can be said about asbestos. This naturally occurring fiber is a great structural fiber that resists heat. However, in the 1970s, scientists found that the dust caused cancer and asbestosis in technicians. Most friction material companies stopped using it, or never touched the asbestos at all because it put not only their customers at risk, but also their own employees.
Some components are not harmful during manufacturing, but during the heat of braking, they can change and even combine with other elements and oxidize.
How harmful is this stuff?
There is no need to purchase a Haz-Mat suit to work on brakes. As long as you use common sense practices, like using a liquid brake cleaner and not compressed air, you should be fine. But, always check the MSDS sheets for any product used in your shop; this includes brake pads.
The main focus of the new laws in Washington state and California is protecting the environment. Much of the dust that is emitted into the air is blown onto areas next to the road, or is washed into the storm drains when it rains. Most storm drains flow directly to creeks, rivers and marine waters without wastewater treatment. Copper and other harmful materials can hurt and kill small marine animals and even render some fish without a sense of smell.
 Contamination always has negative connotations. For brake pads, it has dual meanings. First, it can mean a contaminated friction surfaces that alter friction levels and performance. Second, it can mean contamination to the environment from brake dust.
Contamination always has negative connotations. For brake pads, it has dual meanings. First, it can mean a contaminated friction surfaces that alter friction levels and performance. Second, it can mean contamination to the environment from brake dust.